Its an Ecosystem, Not Just Parts 🤝
The most important rule: PC parts must be compatible. Think of it like a team—everyone needs to speak the same language. Mismatched parts simply wont work together.
The 5-Point Compatibility Check
1. CPU 🧠
Choose your processor first.
CHECK:
Note its Socket Type (e.g., AM5, LGA 1700).
2. Motherboard 🔗
The central hub.
CHECK:
Socket MUST MATCH CPU. Also check RAM Type (DDR5/DDR4).
3. RAM 📝
The workspace.
CHECK:
Type MUST MATCH what the motherboard supports.
4. GPU 👀
The visual powerhouse.
CHECK:
Note its recommended PSU Wattage, Power Connectors, and physical Length.
5. PSU ❤️
The power source.
CHECK:
Wattage must be HIGH ENOUGH for the GPU and have the CORRECT CABLES.
The CPU (The Brain) 🧠
The Central Processing Unit does all the thinking. Think of it as the manager of a company—it delegates tasks and makes sure everything gets done.
AMD Ryzen

Example: Ryzen 7 7800X
- Ryzen 3, 5, 7, 9: Performance Level. Ryzen 5 is the all-rounder, while 7 is for serious gaming and creative work.
- First Number (7): Generation. A higher number means its a newer, more modern chip (e.g., 7xxx is newer than 5xxx).
- Next Numbers (800): Model Rank. Higher is better within the same generation (e.g., a 7800X is faster than a 7700X).
- Socket Type: This is critical. Newer Ryzen 7000+ CPUs use the AM5 socket. Older Ryzen 5000 CPUs (like the 5600X) use the AM4 socket. The CPU socket MUST match the motherboard socket.
- Cooling: High-end CPUs get hot and require a good cooler (sold separately). Mid-range CPUs often include a basic cooler in the box.
- Common Letters:
- X: A slightly faster Xtreme performance version.
- G: Includes basic on-board Graphics, perfect for office PCs that dont need a separate graphics card.
- X3D: Has extra memory stacked on top for the absolute Best Gaming performance.
Intel Core

Example: Core i7-14700K
- Core i3, i5, i7, i9: Performance Level. The i5 is the sweet spot for most users, while the i7 is for high-end gaming and productivity.
- First Numbers (14): Generation. Higher is newer (e.g., 14th gen is newer than 13th gen).
- Next Numbers (700): Model Rank. A higher number is better (e.g., a 14700K beats a 14600K).
- Socket Type: This is critical. Recent 12th, 13th, and 14th Gen CPUs use the LGA 1700 socket. The CPU socket MUST match the motherboard socket.
- Cooling: High-end K series CPUs do not include a cooler and require a good one to be purchased separately to handle their high performance and heat.
- Common Letters:
- K: Unlocked for overclocking, allowing enthusiasts to push it faster. Requires a Z-series motherboard.
- F: Requires a separate Graphics card. A budget-saver if you are buying a gaming card anyway.
- KF: Unlocked AND Requires a separate Graphics card. For enthusiasts on a budget.
The GPU (The Eyes) 👀
The Graphics Card creates the images you see. For gaming, this is the most important part. Its like the design department, responsible for making everything look good.
NVIDIA GeForce
Example: RTX 4070 Ti
- RTX: Modern series with Ray Tracing for realistic lighting in games. Older series was GTX.
- First Number (40): Generation (40-series is newer than 30-series).
- Next Numbers (70): Performance. This is key! 60=Good, 70=Great, 80/90=Best.
- Ti / Super: A stronger, tuned-up version of the base model.
- Physical Size: High-end GPUs can be very long and thick. Always check the cards dimensions against the PC case specs to ensure it will physically fit.
AMD Radeon

Example: RX 7800 XT
- RX: Standard series name for their gaming cards.
- First Number (7): Generation (7xxx is newer than 6xxx).
- Next Numbers (800): Performance Level. Higher is better (7800 > 7700).
- XT / XTX: A more powerful version of the base model.
Intel Arc

Example: Arc A770
- A: The first series/generation from Intels new graphics line.
- First Number (7): Performance Tier (3=Basic, 5=Mid-Range, 7=High-End).
- Next Numbers (70): Model Rank. Higher is better (A770 > A750).
The PC Case (The Skeleton & Skin) 🏠

The case does more than just look good—it protects your expensive components and is essential for good cooling.
Size & Compatibility
The case size must match your motherboard. An ATX motherboard needs an ATX case. You can put a smaller motherboard in a bigger case (e.g., Micro-ATX in an ATX case), but not the other way around.
Airflow & Clearance
A good case will have a mesh front panel to let air in easily. You MUST check the cases specifications to ensure two things: the CPU cooler is not too tall and the Graphics Card is not too long to fit inside.

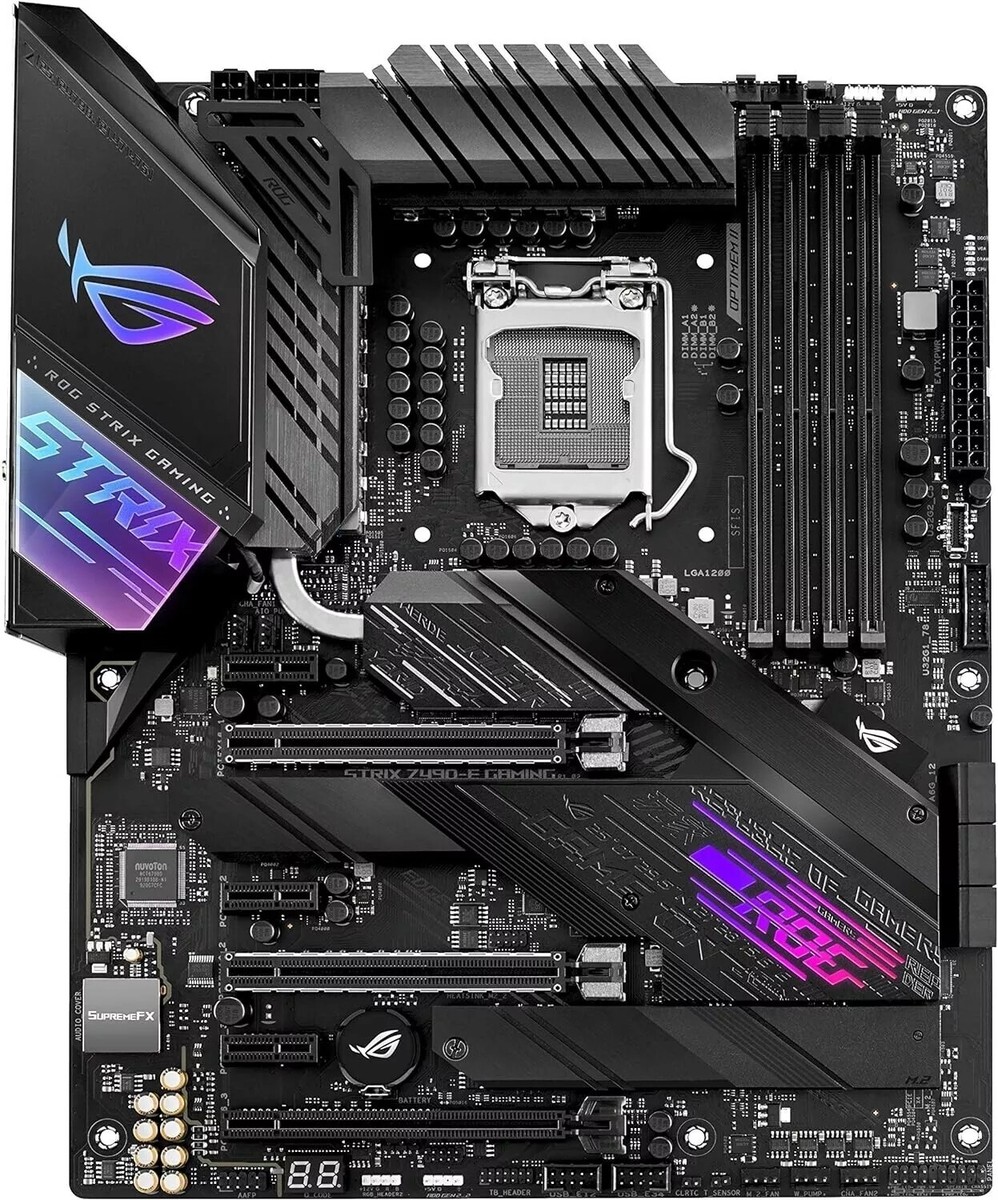
The Motherboard (The Nervous System) 🔗
The motherboard connects everything. The most important job it has is matching the CPU. A CPU will only fit in a motherboard with the correct socket. They are not cross-compatible. For example, an AM4 CPU (Ryzen 5600) will not fit in an AM5 motherboard (B650).
AMD Chipsets
X-Series (e.g., X670): Top-end, for enthusiasts. Best power delivery, supports overclocking, most high-speed ports.
B-Series (e.g., B650): The all-rounder. Great balance of features and price. The best choice for most builds.
A-Series (e.g., A620): Budget-focused. Provides essential features but with fewer ports and basic power delivery.
Intel Chipsets
Z-Series (e.g., Z790): Top-end, for enthusiasts. The only chipset that officially supports CPU overclocking for K model CPUs.
B-Series (e.g., B760): The all-rounder. Excellent features for the price, perfect for non-overclocked systems.
H-Series (e.g., H710): Budget-focused. The basics to get a PC running for office or light use.
The PSU (The Heart) ❤️

The Power Supply Unit provides clean, reliable power. Skimping here is a bad idea—a poor PSU can damage every other part of the PC.
- Brand Matters: Stick to well-reviewed brands (like Corsair, Seasonic, be quiet!). A high-quality PSU is the foundation of a stable system.
- Wattage: MUST be enough for all parts combined, especially the GPU. Use an online PSU Calculator and add ~100W for safety.
- 80+ Rating: Efficiency. A Gold rating is the sweet spot for reliability and saving power.
- Connectors: You MUST check that it has all the cables you need. Look for the right number of PCIe 8-pin connectors for your graphics card.
- Modularity:
- Modular: All cables are detachable. Best for clean builds.
- Semi-Modular: Essential cables are attached, others are optional. A great balance.
- Non-Modular: All cables are permanently attached. Harder to manage.
RAM (The Desk Space) 📝

This is fast, short-term memory for active programs. More RAM is like a bigger desk—you can work on more things at once without slowing down.
- Type (DDR4 vs DDR5): This is the most critical check. The RAM type MUST match what the motherboard supports. DDR5 is newer and faster, but DDR4 is a great budget option. They are not interchangeable.
- Capacity: 16GB (2x8GB sticks) is the minimum for good gaming. 32GB (2x16GB) is the sweet spot for high-end gaming and multitasking.
- Speed (MHz): Higher speed (e.g., 6000MHz) is better, but the sweet spot for price-to-performance is usually around 5600-6000MHz for DDR5.
- XMP / EXPO: A simple setting in the PCs setup menu to make the RAM run at its advertised fast speed. Its like pressing a turbo button for your memory. (XMP for Intel, EXPO for AMD).
Storage (The Filing Cabinet) 🗄️

This is long-term memory where your operating system, games, and files are stored.
- NVMe M.2 SSD: The fastest choice. A small stick that plugs directly into the motherboard for a clean, cable-free look.
- Speed Generations (PCIe): These drives use lanes on a data highway called PCIe. A PCIe 4.0 drive is like having a newer, wider highway than an older PCIe 3.0 drive, allowing for much faster speeds.
- Real-world Impact: A fast NVMe drive makes Windows boot in seconds and dramatically cuts down game loading times.
- Check Compatibility: Ensure the motherboard has a free M.2 slot and supports the drives PCIe generation for maximum speed.
- SATA SSD: A rectangular 2.5-inch drive that connects via a cable.
- Great Value: While not as fast as NVMe drives, they are still massively faster than HDDs.
- Best Use: Perfect as a secondary drive for storing your game library or other large programs affordably.
- HDD (Hard Drive): The slowest and oldest type, using spinning platters.
- Bulk Storage: Because its very cheap per gigabyte, its the best option for mass storage of files where speed isnt critical, like photos, videos, and documents.
The CPU Cooler (The Radiator) ❄️
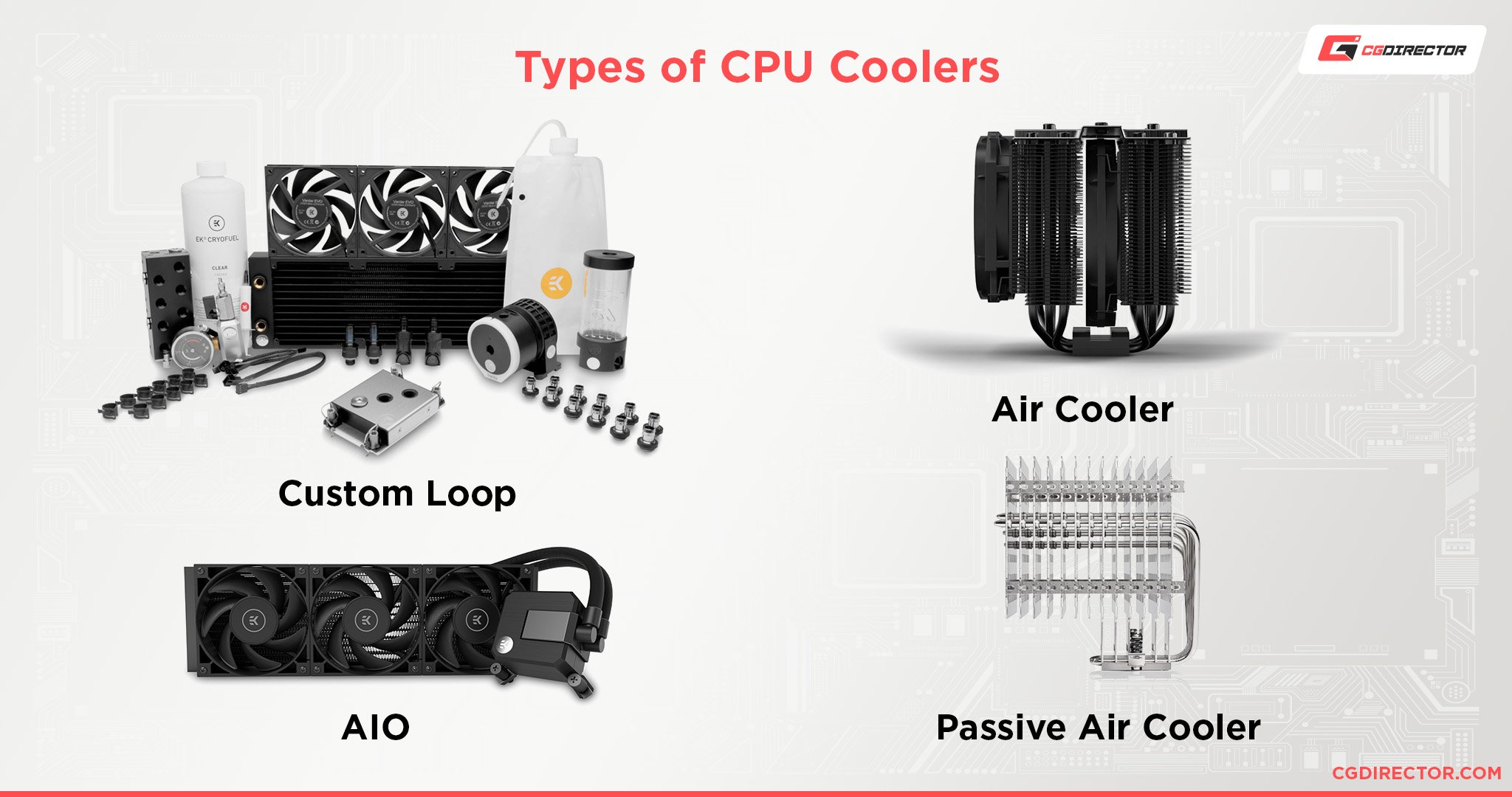
High-performance CPUs generate a lot of heat. A coolers job is to pull that heat away to prevent the CPU from slowing down (throttling) or getting damaged.
- Air Cooler: A metal heatsink with fins and a fan. They are simple, very reliable, and offer fantastic performance for the price.
- AIO Liquid Cooler: Uses a pump to circulate liquid from the CPU to a radiator with fans. They often provide the best possible cooling performance and can have a cleaner aesthetic.
- Compatibility: You must check that the cooler is compatible with your CPUs socket type (e.g., AM5, LGA 1700). You also need to check its height (for air coolers) or radiator size (for AIOs) to ensure it fits in your PC case.
Putting It All Together: A Real-World Layout
This diagram uses a real motherboard to show you exactly where components go.
